Breaking the Slouch: Conquer Bad Posture for a Healthier You!
In our increasingly sedentary lifestyles, one aspect that often goes unnoticed but significantly impacts our well-being is our posture. Whether it's hours spent hunched over desks or slouched on couches, bad posture has become an epidemic in the digital age. But fear not! This blog post aims to shed light on the detrimental effects of poor posture and provide practical tips to help you straighten up and regain control of your health. So, let's dive in and explore the fascinating world of posture correction.
Negative Impacts of Bad Posture
Bad posture can have a wide range of negative consequences on both our physical and mental well-being. Here are some common consequences associated with poor posture:
1. Chronic Back, Neck, and Shoulder Pain: Slouching or hunching forward for extended periods places excessive strain on the muscles and ligaments of the back, neck, and shoulders. This can lead to chronic pain, stiffness, and discomfort.2. Reduced Spinal Alignment: Poor posture can disrupt the natural alignment of the spine, causing imbalances and misalignments. Over time, this can lead to conditions like scoliosis or kyphosis, where the spine curves abnormally.
3. Decreased Lung Capacity: Slouching compresses the chest cavity, restricting the space available for the lungs to expand fully. As a result, the lungs may not receive an adequate amount of oxygen, leading to reduced lung capacity and potentially affecting overall respiratory health.
4. Digestive Issues: Slumping forward compresses the abdominal organs, potentially compromising their function. This compression can contribute to issues such as slowed digestion, acid reflux, and constipation.
5. Headaches and Jaw Problems: Poor posture, especially forward head posture, can strain the muscles in the neck and upper back. This muscle tension can lead to headaches, migraines, and even temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, causing jaw pain and difficulty in opening or closing the mouth.
6. Fatigue and Reduced Energy Levels: Slouched posture restricts the flow of oxygen and blood throughout the body, which can result in decreased energy levels and increased feelings of fatigue.
7. Poor Athletic Performance: Bad posture affects the alignment and coordination of muscles, impacting athletic performance. It can decrease stability, balance, and overall efficiency of movement, potentially leading to decreased performance and increased risk of injuries.
8. Negative Impact on Mood and Self-Confidence: Research suggests that poor posture can have psychological consequences. Slumping or closed-off body language can affect our mood, self-esteem, and even our interactions with others. Conversely, adopting an upright, confident posture can enhance mood and boost self-confidence.
9. Impaired Digestion: Poor posture can compress the digestive organs, leading to issues like slowed digestion, acid reflux, and constipation.
10. Impaired Circulation: Slouching or crossing legs for prolonged periods can restrict blood flow, potentially leading to poor circulation. Reduced blood flow may contribute to various health issues, including swollen legs and feet, cold hands, and increased risk of blood clots.
Understanding the consequences of bad posture highlights the importance of prioritizing good posture habits and making conscious efforts to improve alignment throughout the day. By doing so, we can help prevent these negative effects and maintain a healthier, more comfortable lifestyle.
Causes of Bad Posture
Understanding the root causes of bad posture is crucial for effectively addressing and correcting the issue. Here are some common factors that contribute to poor posture:
1. Sedentary Lifestyle: The modern sedentary lifestyle, characterized by long hours of sitting or remaining in static positions, is a major contributor to bad posture. Sitting for extended periods without breaks or engaging in regular physical activity weakens the muscles that support good posture, leading to slouching or hunching forward.2. Improper Ergonomics: Incorrect workstation setups, such as poorly adjusted chairs, desks, or computer monitors, can significantly impact posture. Inadequate support or improper alignment while working can strain the muscles and joints, encouraging poor posture habits.
3. Weak Muscles: Weak core muscles, including the abdominals, back muscles, and pelvic floor muscles, play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. When these muscles are weak or imbalanced, they are unable to provide adequate support, leading to postural imbalances.
4. Lack of Body Awareness: Many people are simply unaware of their posture or do not pay attention to their body alignment throughout the day. This lack of body awareness can allow poor posture habits to develop and persist.
5. Stress and Emotional Factors: Emotional stress and psychological factors can influence posture. Stress and tension can cause individuals to hunch their shoulders, tighten their neck muscles, or adopt defensive postures, leading to poor alignment over time.
6. Incorrect Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects with improper technique, such as lifting with the back instead of using leg muscles, can strain the spine and contribute to postural problems.
7. Excessive Weight: Carrying excess weight, particularly in the abdominal area, can disrupt the body's natural alignment and place additional strain on the spine. This can contribute to poor posture and increase the risk of developing musculoskeletal issues.
8. Genetics and Body Structure: Some individuals may have inherent structural factors that make them more prone to poor posture, such as spinal abnormalities or imbalances in muscle length or flexibility.
9. Repetitive Movements: Engaging in repetitive motions or activities without proper form or rest can lead to muscle imbalances and postural issues. This is commonly seen in occupations or hobbies that involve repetitive tasks or asymmetrical movements.
By understanding these root causes, individuals can begin to address and correct their posture. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, ergonomic adjustments, targeted exercises to strengthen weak muscles, and cultivating body awareness and mindfulness throughout daily activities. Taking proactive steps to address these causes can lead to improved posture and overall well-being.
Exercises & Tips to Fix Bad Posture
Fixing bad posture requires a combination of exercises, mindful adjustments, and consistent habits. Here are some exercises and tips to help improve your posture:
1. Shoulder Blade Squeezes:
Sit or stand tall with your arms by your sides. Squeeze the blades of your shoulder together and hold for 5 to 10 seconds. Repeat this exercise multiple times throughout the day to strengthen the muscles that retract and stabilize the shoulders.
2. Wall Angels:
Stand with your back against a wall, feet hip-width apart, and arms bent at 90 degrees with your elbows and wrists touching the wall. Slowly slide your arms up and down the wall, maintaining contact with your elbows, wrists, and back at all times. This exercise helps improve shoulder mobility and upper back posture.
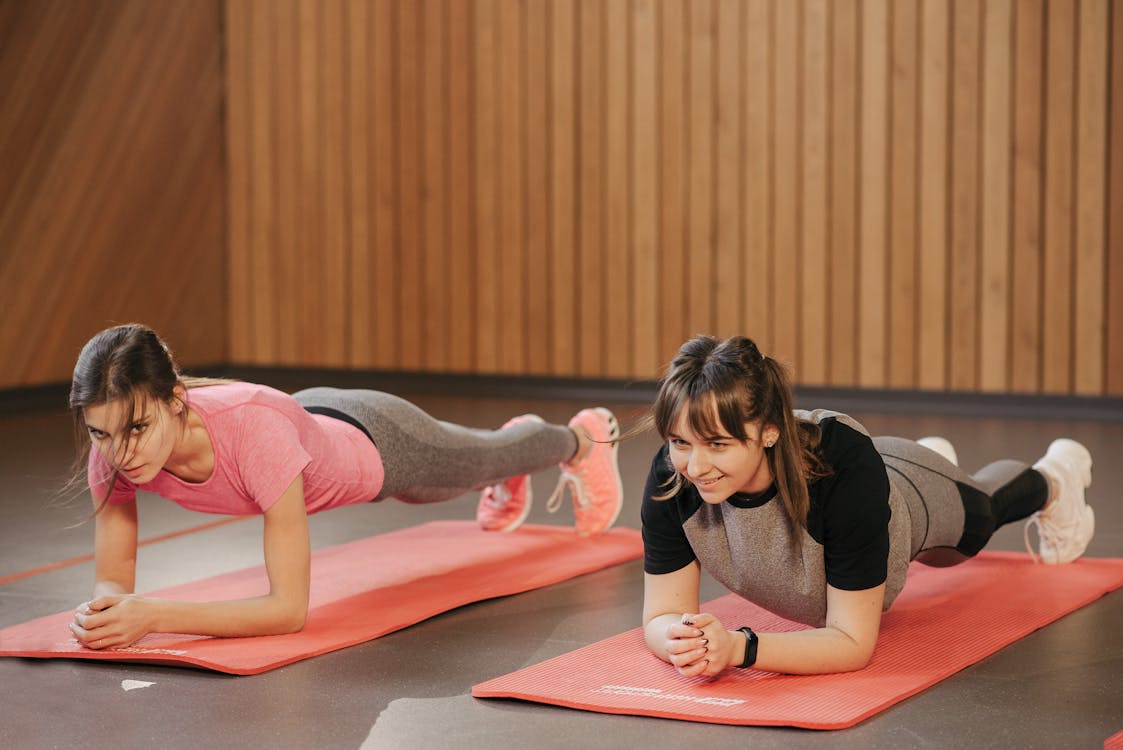
3. Core-Strengthening Exercises:
Engaging and strengthening your core muscles provides stability and supports good posture. Incorporate exercises like planks, bird dogs, and abdominal crunches into your routine to strengthen your abdominals, back muscles, and deep core stabilizers.
4. Chin Tucks:
Sit or stand with your spine straight. Gently retract your chin by tucking it back, as if you're making a double chin. Hold for a few seconds and repeat. This exercise helps in counteracting forward the head posture and makes the muscles at the front of the neck strong.
5. Thoracic Extensions:
Sit on the edge of a chair and interlace your fingers behind your head, elbows out to the sides. Gently arch your upper back, leaning backward over the back of the chair. Hold that position for a few seconds and repeat the exercise several times. This exercise helps improve thoracic spine mobility and counteracts rounded upper back posture.
6. Stretching Chest and Hip Flexor Muscles:
Tight chest muscles and hip flexors can contribute to poor posture. Perform stretches like the chest stretch (interlace fingers behind your back and gently lift arms) and hip flexor stretch (lunge forward with one leg and gently lean forward) to lengthen these muscles and promote better posture.
7. Mindful Posture Checks:
Set reminders throughout the day to check your posture. Pay close attention to how you stand, move, and sit. Align your head, shoulders, and hips in a straight line, engage your core, and avoid slouching or hunching forward.
8. Ergonomic Adjustments:
Ensure your workstation is ergonomically optimized. Adjust your chair height, and desk height, and monitor position to support good posture. Use a lumbar roll or pillow for lower back support and ensure your feet are flat on the ground or supported by a footrest.
9. Body Awareness and Mindfulness:
Cultivate body awareness throughout the day. Be mindful of your posture during various activities, such as walking, lifting, or using electronic devices. Practice mindfulness to reduce stress and tension, which can impact your posture.
10. Regular Movement Breaks:
Take frequent breaks from prolonged sitting or sedentary activities. Stand up from your place, move around, and stretch after every 30 minutes. Incorporate light exercises or walks into your breaks to promote blood circulation and reduce postural strain.
Remember, correcting bad posture takes time and consistency. Be patient with yourself and maintain a consistent routine of exercises and mindful adjustments. Gradually, you will notice improvements in your posture and overall well-being. If you have severe or persistent postural issues, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
In conclusion, bad posture is a pervasive problem in our modern sedentary lives, with far-reaching consequences for our physical and mental well-being. The good news is that by understanding the negative effects of poor posture and taking proactive steps, we can correct and improve our alignment.
Throughout this blog post, we explored the hidden consequences of bad posture, delved into its root causes, and outlined a roadmap for posture correction. From developing body awareness and practicing ergonomics to strengthening core muscles and incorporating targeted exercises, every step along the way contributes to better posture and a healthier body.
Remember that correcting bad posture requires consistency, patience, and a holistic approach. It's not an overnight transformation but a journey that involves conscious effort and mindful adjustments in our daily lives. By incorporating the recommended exercises, mindful posture checks, ergonomic adjustments, and healthy habits, you can gradually reverse the effects of poor posture and reap the benefits of improved alignment.
So, let's straighten up and embrace the path to better posture. Stand tall, sit upright, and move with grace and awareness. By taking charge of our posture, we not only enhance our physical health but also boost our confidence, mood, and overall well-being.
Make a commitment to yourself today and embark on the journey to better posture. Your body will thank you, and you'll discover the incredible transformation that comes with standing tall and aligning yourself with optimal health and vitality.
Remember, the power to correct your posture lies within you. Start now, and embrace the transformative effects of good posture on your life.








Comments
Post a Comment